Desarrollo de Materiales para Aplicaciones Marítimas, Fluviales y Militares
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.25043/19098642.164Palabras clave:
Materiales Compuestos, Diseño de Materiales, aplicaciones Militares, Mecanismos de Disipación de Energía de Impacto, Aplicaciones Navales y FluvialesResumen
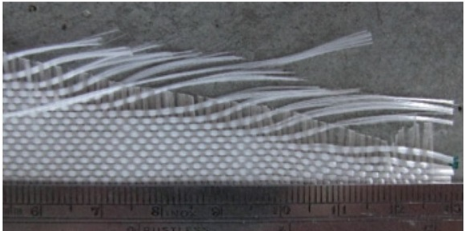
Utilizando los múltiples mecanismos de disipación de la energía de impacto a alta velocidad, hemos desarrollado una plataforma de diseño de materiales compuestos de matriz polimérica, especiales para aplicaciones militares en navegación fluvial y marítima. Nuestros compuestos pretenden hacer sinergia entre las capacidades de disipación de cerámicos y fibras de alto desempeño, los cuales son utilizados como los elementos de refuerzo en los laminados de bajo peso. El diseño del material es combinado con herramientas de procesamiento y técnicas avanzadas de caracterización que resultan en laminados consistentes de alta repetibilidad, trazabilidad y alta calidad. La plataforma parte de la identificación de los mecanismos de disipación y de una caracterización detallada de la resina polimérica, el cual incluye un diagrama de Tiempo-Temperatura-Transformación que provee las condiciones óptimas de procesamiento. Nuestros diseños abren rutas novedosas para aplicaciones militares, los cuales incluyen amplios portafolios de protección, versatilidad geométrica, resistencia mecánica y confiabilidadDescargas
Referencias bibliográficas
ZUKAS, J.A., NICHOLAS, T., SWIFT, H., GRESZCZUK, L.B., CURRAN, D.R. Impact Dynamics. John Wiley & Sons, USA 1982, 452p.
SRIVATHSA, B., RAMAKRISHNAN, N. (1999). Ballistic performance maps for thick metallic armour. Journal of Materials Processing Technology 96, 81-91.
DEMIR, T., UBEYLI, M., YILDIRIM, R.O. (2008). Investigation on the ballistic impact behavior of various alloys against 7.62 mm armor piercing projectile. Materials and Design 29, 2009-2016.
OZSAHIN, E., TOLUN, S. (2010). Influence of surface coating on ballistic performance of aluminum plates subjected to high velocity impact loads. Materials and Design 31, 1276-1283.
OZSAHIN, E., TOLUN, S. (2010). On the comparison of the ballistic response of coated aluminum plates. Materials and Design 31, 3188-3193.
BORVIK, T., FORRESTAL, M.J., HOPPERSTAD, O.S., WARREN, T.L., LANGSETH, M. Perforation of AA5083-H116 aluminium plates with conical-nose steel projectiles - Calculations. International Journal of Impact Engineering 36 (2009) 426-437.
BORVIK, T.,CLAUSEN, A.H., HOPPERSTAD, O.S., LANGSETH, M. Perforation of AA5083-H116 aluminium plates with conical-nose steel projectiles— experimental study. International Journal of Impact Engineering 30 (2004) 367-384.
DEY, S., B0RVIK, T., HOPPERSTAD. O.S., LANGSETH, M. On the influence of constitutive relation in projectile impact of steel plates. International Journal of Impact Engineering 34 (2007) 464-48.
DEY, S., B0RVIK, T., HOPPERSTAD. O.S., LANGSETH, M. On the influence of fracture criterion in projectile impact of steel plates. Computational Materials Science 38 (2006) 176-191.
UBEYLI, M., DEMIR, T., DENIZ, H., YILDIRIM,R.O., KELES, O. Investigation on the ballistic performance of a dual phase steel against 7.62mm AP projectile. Materials Science and Engineering A 527 (2010) 20362044.
MISHRA,B.,JENA,P.K.,RAMAKRISHNA, B., MADHU, V., BHAT, T.B., GUPTA, N.K. Effect of tempering temperature, plate thickness and presence of holes on ballistic impact behavior and ASB formation of a high strength steel. International Journal of Impact Engineering 44 (2012) 17-28.
MEDVEDOVSKI, E. (2001). Wear-resistant engineering ceramics. Wear 249, 821-828.
NAIK, N.K., SHRIPAO, P., REDDY, B.C.K. (2006) Ballistic impact behaviour of woven fabric composites: Formulation. International Journal of Impact Engineering 32, 1521-1552.
HOO-FATT M.S., SIRIVOLU, D. (2010). A wave propagation model for the high velocity impact response of a composite sandwich panel. International Journal of Impact Engineering 37, 117-130.
REYES, G., CANTWELL, W.J. (2004). The high velocity impact response of composite and FML-reinforced sandwich structures. Composites Science and Technology 64, 35-54.
GRUJICIC, M., ARAKERE, G., HE, T., BELL, W.C., CHEESEMANB, B.A., YENB, C.F., SCOTT, B. (2008). A ballistic material model for cross-plied unidirectional UHMWPE fiber-reinforced armor-grade composites. Materials Science and Engineering A 498, 231-241.
Technical Guide Kevlar - Aramid Fiber. DuPond, 32p: www.kevlar.com.
LANE, R. High Performance Fibers for Personnel and Vehicle Armor Systems-Putting a Stop to Current and Future Threats. AMPTIAC Rome, NY: http://ammtiacalionscience.com/pdf/AMPQ9_2ART01.pdf
Tawron - a versatile high-performance fiber. TEIJIN, 7p: http://www.teijinaramid.com/aramids/twaron/
Technora. TEIJIN: http://www.teijinaramid.com/aramids/technora/
Honeywell Gold Shield® GV-2016: www. honeywell.com/spectra
Dyneema: http://www.dyneema.com/americas/applications/life-protection.aspx
POB Fiber Zylon. TOYOBO CO., LTD, 18p: www.toyobo.co.jp
MEDVEDOVSKI, EUGENE. Alumina- mullite ceramics for structural applications. Ceramics International 32 (2006) 369-375.
MEDVEDOVSKI, EUGENE. Ballistic performance of armour ceramics: Influence of design and structure. Part 1. Ceramics International 36 (2010) 2103-2115.
MEDVEDOVSKI, EUGENE. Ballistic performance of armour ceramics: Influence of design and structure. Part 2. Ceramics International 36 (2010) 2117-2127.
KARAMIS, M.B. Tribology at high-velocity impact. Tribology International 40(2007) 98-104.
KARAMIS, M.B., NAIR, F., CERIT, A.A. The metallurgical and deformation behaviours of laminar metal matrix composites after ballistic impact. Journal of Materials Processing Technology 209 (2009) 4880-4889.
KARAMIS, M.B., CERIT, A.A., NAI, F. Surface characteristics of projectiles after frictional interaction with metal matrix composites under ballistic condition. Wear 261 (2006) 738-745.
GAMA, B.A., GILLESPIE, J.W. Punch shear based penetration model of ballistic impact of thick-section composites. Composite Structures 86 (2008) 356-369.
XIAO, J.R., GAMA, B.A., GILLESPIE, J.W. Progressive damage and delamination in plain weave S-2 glass/SC-15 composites under quasi-static punch-shear loading. Composite Structures 78 (2007) 182-196.
ERKENDIRCI, O.F., (GAMA) HAQUE, B.Z. Quasi-static penetration resistance behavior of glass fiber reinforced thermoplastic composites. Composites: Part B xxx (2012) xxx-xxx
MORYE, S.S., HINE, P.J., DUCKETT, R.A., CARR, D.J., WARD, I.M. Modelling of the energy absorption by polymer composites. Composites Science and Technology 60 (2000) 2631-2642.
Lightweight ballistic composites - Military and Law enforcement applications. Edited by Ashok Bhatnagar. Woohead Publishing Limited, Cambridge, England, 2006, 428p.
SARVA, S., NEMAT-NASSER, S., MCGEE, J., ISAACS, J. The effect of thin membrane restraint on the ballistic performance of armor grade ceramic tiles. International Journal of Impact Engineering 34 (2007) 277-302.
QUN WANG, ZHAOHAI CHEN, ZHAOFENG CHEN. Design and characteristics of hybrid composite armor subjected to projectile impact. Materials and Design 46 (2013) 634-639.
CORRAN, R.S.J., SHADBOLT, P.J., RUIZ, C. Impact Loading of Plates - An Experimental Investigation. Int. J. Impact. Engng. Vol 1 No. 1 (1983) pp3-22.
Dey, S., Borvik, T., Teng, X., Wierzbicki, T., Hopperstad, O.S. On the ballistic resistance of double layered steel plates: An experimental and numerical investigation. International Journal of Solids and Structures 44 (2007) 6701-6723.
HOCKAUF, M., MEYER, L.W., PURSCHE, F., DIESTEL, O. Dynamic perforation and force measurement for lightweight materials by reverse ballistic impact. Composites: Part A 38 (2007) 849 - 857.
FLORES, A., ANIA, F., BALTÁ-CALLEJA, F.J. From the glassy state to ordered polymer structures: A microhardness study. Polymer 50 (2009) 729-746.
Descargas
Publicado
Número
Sección
Licencia
The authors who publish in this Journal certify that:
- The work submitted for publication in The Ship Science and Technology journal, was written by the author, given that its content is the product of his/her direct intellectual contribution.
- All data and references to material already published are duly identified with their respective credits and are included in the bibliographic notes and quotations highlighted as such.
- All materials submitted for publication are completely free of copyrights; consequently, the author accepts responsibility for any lawsuit or claim related with Intellectual Property Rights thereof, Exonerating of responsibility to The Science and Technology for the Development of Naval, Maritime, and Riverine Industry Corporation, COTECMAR.
- In the event that the article is chosen for publication by The Ship Science and Technology journal, the author state that he/she totally transfers reproduction rights of such to The Science and Technology for the Development of Naval, Maritime, and Riverine Industry Corporation, COTECMAR.
- The authors retain the copyright and transfer to COTECMAR the right of publication and reproduction of the work which will be simultaneously subject to the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC - BY), which allows the license to copy, distribute, display and represent the work and to make derivative works as long as it recognizes and cites the work in the manner specified by the author or licensor.
- For more information about the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC -BY) and his use and scope, please visit the following web page https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/legalcode