Análisis estructural de un Multicasco de aluminio
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.25043/19098642.123Palabras clave:
Multicasco, análisis estructural, elementos finitosResumen
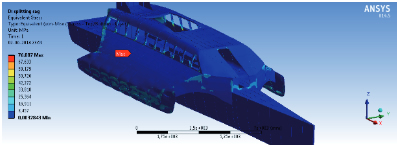
El análisis estructural de un multicasco es relativamente complejo debido a que la estructura de unión entre los cascos introduce esfuerzos adicionales a los típicos de un monocasco. El trimarán de aluminio presentado en este trabajo fue diseñado en el marco del proyecto de investigación “Diseño Conceptual de Embarcación de Alto Desempeño para el Transporte de Pasajeros en la Zona Austral de Chile”. El trimarán se dimensionó estructuralmente usando los reglamentos de las sociedades de clasificación Germanischer Lloyd, Det Norske Veritas y Lloyd´s Register. Para el escantillonado obtenido con cada reglamento se creó un Modelo de Elementos Finitos y el análisis estructural se llevó a cabo para los eventos de slamming y splitting moment. Se analizaron los resultados y se determinaron las zonas de concentración de esfuerzos para compararlos con los esfuerzos admisibles y concluir si el dimensionamiento estructural responde en forma adecuada y segura a las cargas de diseño.
Descargas
Referencias bibliográficas
ANSYS, Teoría de Referencia Ansys, Version 14.5, Canonsburg: Ansys, Inc., 2011
BLANCHARD T. Y CHUNHUA, G.; «Rules for the Classification of Trimarans» Naval Engineers Journal, vol. 44, pp. 1 -50, 2007.
CHENG F. Y MAYOSS, C.; The development of Trimaran rules, London: Lloyd´s Register, 2007.
DET NORSKE VERITAS AS, Rules for classification of high speed, light craft and naval surface craft, Oslo: Det Norske Veritas, 2012.
GERMANISCHER LLOYD, Rules for Classification and construction, High Speed Craft., Hamburg: Germanischer Lloyd, 2002.
LLOYD´S REGISTER, Rules and Regulations for the classification of Trimarans Rules, London: Lloyd´s Register, 2006.
MORRIS, J.; «A three dimensional structural analysis of a large wave piercing catamaran design,» High speed marine transportation IMAS 91, pp. 89 - 102, 1991.
OJEDA, R.; GANGADHARA, B.; Y SALAS, M.;«Finite element investigation on the static response of a composite catamaran under slamming loads,» Ocean Engineering, vol. 31, pp. 901 -929, 2004.
PAIK, J. Y HUGHES, O.; «Ultimate limit state design technology for aluminium multi - hull ship strcture,» SNAME Transactions , vol. 113, pp. 270 - 305, 2006
TAMPIER, G.; Informe Final Proyecto Perfil I+D Aplicada CORFO 13IDL1-18236., Valdivia, 2013.
Descargas
Publicado
Número
Sección
Licencia
The authors who publish in this Journal certify that:
- The work submitted for publication in The Ship Science and Technology journal, was written by the author, given that its content is the product of his/her direct intellectual contribution.
- All data and references to material already published are duly identified with their respective credits and are included in the bibliographic notes and quotations highlighted as such.
- All materials submitted for publication are completely free of copyrights; consequently, the author accepts responsibility for any lawsuit or claim related with Intellectual Property Rights thereof, Exonerating of responsibility to The Science and Technology for the Development of Naval, Maritime, and Riverine Industry Corporation, COTECMAR.
- In the event that the article is chosen for publication by The Ship Science and Technology journal, the author state that he/she totally transfers reproduction rights of such to The Science and Technology for the Development of Naval, Maritime, and Riverine Industry Corporation, COTECMAR.
- The authors retain the copyright and transfer to COTECMAR the right of publication and reproduction of the work which will be simultaneously subject to the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC - BY), which allows the license to copy, distribute, display and represent the work and to make derivative works as long as it recognizes and cites the work in the manner specified by the author or licensor.
- For more information about the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC -BY) and his use and scope, please visit the following web page https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/legalcode