Modelado numérico de la propagación de fractura por fatiga utilizando el método de los elementos de contorno
Keywords:
Fracture growth propagation, boundary element method, fracture mechanicsAbstract
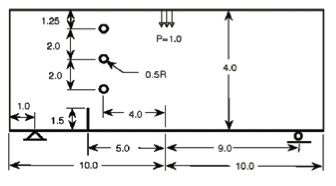
The work presents a computer tool based on the boundary element method (BEM), that allows the study of the propagation of fracture phenomenon in structures which have sustained cyclical efforts. The code functions to develop computer models focused on the study of residual resistance of fractured bi-dimensional components based on linear elastic fracture mechanics (LEFM). The boundary element formulation of the problem is presented, as well as its computer implementation and its application to the specific problem analysis of fracture growth by fatigue. Fracture growth is modeled through the theory proposed by Paris, applied to the case of flat elasticity, and the criteria of maximum main efforts is used to define the direction of propagation (Portela, 1992). The BEM formulation was implemented in a computer code developed in Matlab 7.0 . The program has demonstrated effectiveness in predicting trajectories of propagation and residual resistance by fatigue, allowing its use as a tool of analysis in engineering.Downloads
References
Aliabadi,M. H.; Rooke, D. P. (1992) Numerical Fracture Mechanics, Southampton, Computa-tional Mechanics Publications, Elsevier.
Aoki, S.; Hasebe, N. (1987) Stress Intensity Factors Handbook, New York, Pergamon Press.
Brebbia, C. A.; Domínguez, J. (1989) Boundary Elements an Introductory Course, New York, McGraw-Hill.
Bittencourt, T. N., Wawrzynek, P. A., Ingraffea, A. R. (1996) “Quasi-Automatic Simulation of Crack Propagation for 2D LEFM problems”, Engineering Fracture Mechanics, vol. 55, n.o 2, pp. 321-334.
Broek, D. (1986) Elementary Engineering Fracture Mechanics, The Netherlands, Martinus Nijhoff Publishers, Dordrecht.
Dirgantara, T. (2002) Boundary Element Analysis of Cracks in Shear Deformable Plates and Shells, Southampton, WIT press.
Meguid, S. A. (1989) Engineering Fracture Mecha-nics, New York, Elsevier.
Patridge, P. W.; Brebbia, C. A.; Wrobel, L. C. (1992), The dual reciprocity boundary element method, Southampton, Computational mecha-nics publications, Elsevier.
Portela, A. (1992) Dual Boundary Element Incremental Analisis of Crack Growth [tesis doctoral], Southampton, Wessex Institute of Techonology.
Portela, A.; Aliabadi, M. A. (1992) “The Dual Boundary Element Method: Effective Implementation for Crack Problems”, International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, vol. 33, pp. 1269-1297.
Downloads
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
The authors who publish in this Journal certify that:
- The work submitted for publication in The Ship Science and Technology journal, was written by the author, given that its content is the product of his/her direct intellectual contribution.
- All data and references to material already published are duly identified with their respective credits and are included in the bibliographic notes and quotations highlighted as such.
- All materials submitted for publication are completely free of copyrights; consequently, the author accepts responsibility for any lawsuit or claim related with Intellectual Property Rights thereof, Exonerating of responsibility to The Science and Technology for the Development of Naval, Maritime, and Riverine Industry Corporation, COTECMAR.
- In the event that the article is chosen for publication by The Ship Science and Technology journal, the author state that he/she totally transfers reproduction rights of such to The Science and Technology for the Development of Naval, Maritime, and Riverine Industry Corporation, COTECMAR.
- The authors retain the copyright and transfer to COTECMAR the right of publication and reproduction of the work which will be simultaneously subject to the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC -BY) , which allows the license to copy, distribute, display and represent the work and to make derivative works as long as it recognizes and cites the work in the manner specified by the author or licensor.
- For more information about the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC -BY) and his use and scope, please visit the following web page https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/legalcode